
파이썬은 객체지향 프로그래밍을 위한 언어입니다. 우리는 이제 객체라는 개념을 배웠고 이 객체를 실제 코드에서 어떻게 구현하는지 배웠습니다.
객체라는 개념을 쓴다는 사실 하나만으로 객체지향 프로그래밍이 정의되는 건 아닙니다. 기존의 절차지향 프로그래밍과 확연히 다른 특징이 필요하죠.
객체지향 프로그래밍만의 특징은 크게 5가지가 있습니다.
우린 이미 추상화에 대해서 배웠습니다. 객체라는 개념을 배우는 순간부터 추상화에 대해서 배운 겁니다.
Bread라는 Class를 작성할 때도. 우린 여러 빵들이 가진 특징 중에서 ‘모든 빵은 이름이 있다’라는 공통적인 사실을 알고 있습니다. 이런 공통적인 특징을 추출해서 코드로 만들었습니다.
class Bread:
def __init__(self):
self.name = name
이 과정에서 우린 캡슐화도 이미 배웠습니다. 캡슐화는 데이터(속성)와 데이터를 처리하는 메소드를 하나로 묶은 것을 의미합니다.
아래 코드처럼 name, num_of_ingredients라는 Attribute와 print_bread_info를 하나로 묶어서 처리했습니다.
class Bread:
def __init__(self, name, num_of_ingredients):
self.name = name
self.num_of_ingredients = num_of_ingredients
def print_bread_info(self):
print("name: {}, ingreNums: {}".format(self.name, self.num_of_ingredients))
코드를 제시하기 전에 한 번 만들어보세요. 아래의 클래스 다이어그램과 파일들, 실행코드를 보고 만들어보세요.
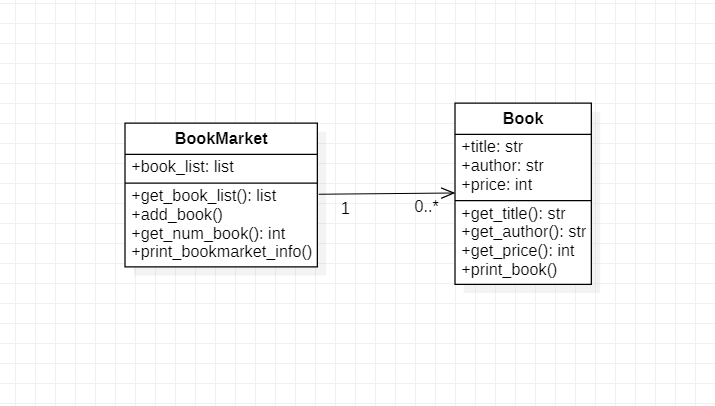
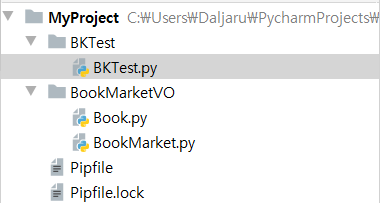
from BookMarketVO.Book import Book
from BookMarketVO.BookMarket import BookMarket
if __name__ == '__main__':
book1 = Book('Little Women','Louisa May Alcott', '20000')
book2 = Book('Harry Potter', 'J. K. Rowling', '15000')
bookList = []
bookList.append(book1)
bookList.append(book2)
book_market = BookMarket(bookList)
print(book_market.print_bookmarket_info())
#결과
#Market's book list. total : 2
#title: Little Women, author : Louisa May Alcott, price: 20000
#title: Harry Potter, author : J. K. Rowling, price: 15000
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
class Book:
def __init__(self, title, author, price):
self.title = title
self.author = author
self.price = price
def get_title(self):
return self.title
def get_author(self):
return self.author
def get_price(self):
return self.price
def print_book(self):
print("title: {}, author : {}, price: {}".format(self.title, self.author, self.price))
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
class BookMarket:
def __init__(self):
pass
def __init__(self, book_list):
self.book_list = book_list
def get_book_list(self):
return self.book_list
def add_book(self, book):
self.book_list.append(book)
def get_num_books(self):
return len(self.book_list)
def print_bookmarket_info(self):
print("Market's book list. total : {}".format(len(self.book_list)))
for book in self.book_list:
book.print_book()
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass