
앞에서 print(‘Hello world’)에서 우리는 이미 문자열 객체를 다루었습니다. 문자열은 아래와 같은 규칙을 가지고 있습니다.
str1 = 'Hello World' #작은따옴표와 큰따옴표를 둘다 쓸 수 있습니다.
str2 = "Hello World"
str3 = """I can study python now
it is really easy""" # 따옴표 세개는 여러줄의 문자열을 만들 수 있습니다.
print(str1)
print(str2)
print(str3)
문자열은 크게 보면 Sequence Type입니다. Sequence Type은 음이 아닌 정수로 인덱싱(indexing)될 수 있는 유한한 길이의 순서 있는 집합을 나타냅니다.
문자열로 보면 다음과 같습니다.
if __name__ == '__main__': # Line1
str = "This is test string."
print(str[0])
print(str[1])
print(str[2])
for i in range(len(str)): #Line8 반복문입니다.
print(str[i], end='')
아직 Line1과 Line8이 뭔지는 모르지만 일단 써봅시다.
Index를 이용해 Sequence의 개별항목에 접근할 때는 ‘[’ 와 ]’ 사이에 Index를 넣습니다.
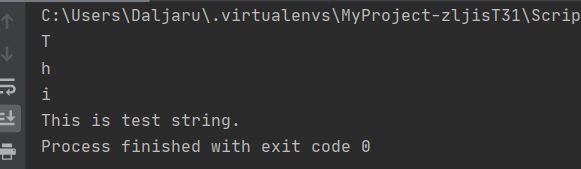
여기서 str이라는 변수에 “This is test string”이라는 변수를 넣었고 str[0]을 출력하니 T, str[1]을 출력하니 h, str[2]를 출력하니 i가 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 만약 눈치가 빠르다면 맨 마지막 ‘.’을 출력하기 위해 어떻게 해야하는지 알 수 있을 것입니다. str[문자열의 전체길이 - 1]을 해주면 되겠죠.
Line8은 반복문을 이용해 문자열을 인덱스를 통해 출력해보았습니다.
아직 Line8이 뭔진 모르지만 딱 문자열의 길이만큼 반복했다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
문자열에서 공통시퀀스연산을 코딩해보겠습니다.
Sequence타입들이 가지고 있는 연산들이 있습니다. 이를 공통시퀀스연산이라고 하는데 몇가지 자주 쓰이는 것만 알아보겠습니다.
if __name__ == '__main__':
testString = "This is test string."
문자열이 있는지 확인
print('t' in testString) # True
print('z' in testString) # False
print('Th' in testString) # True
print('t' not in testString) # False
print('z' not in testString) # True
print('Th' not in testString) #False
문자열 붙이기
addString = " It works well."
testString = testString + addString
print(testString) #This is test string. It works well.
여러번 출력하기
testString = testString * 2 #or 2 * testString
print(testString) #This is test string.This is test string.
슬라이싱
print(testString[0:6]) #This i 0번재 index부터 문자 6개 출력
문자열의 길이
print(len(testString)) #20
문자열에서 특정 문자열의 개수
print(testString.count('is')) #2
if __name__ == '__main__':
str1 = "This is test string."
모두 대문자로 만들기
str1 = str1.upper()
print(str1) #THIS IS TEST STRING.
모두 소문자로 만들기
str1 = str1.lower()
print(str1) #this is test string.
대문자를 소문자로, 소문자를 대문자로.
str1 = str1.swapcase()
print(str) #tHIS IS TEST STRING.
문자열을 분리해서 리스트에 넣기
str2 = str1.split() #공백을 기준으로 분리
print(str2) #['This', 'is', 'test', 'string.']
str2 = str1.split('s') #'s'문자를 기준으로 분리.
print(str2) #['Thi', ' i', ' te', 't ', 'tring.']
지정한 문자열이 몇개 있는지 확인하기
number = str1.count('is')
print(number) #2
알파벳이 맞는지 확인하기
str1 = 'This is test string'
str2 = 'apple'
print(str1.isalpha()) #False 문자열에 공백이 들어가서 false
print(str2.isalpha()) #True 오로지 apple알파벳만 있으므로 true
비슷한 것들로 오른쪽 메소드들이 있습니다. isalpha(), isdecimal(), isdigit(), isnumeric().